Monkeypox: Signs and Symptoms
Monkeypox is a rare disease caused by infection with the monkeypox virus. Monkeypox virus is part of the same family of viruses as variola. It is now being reported in some states in Nigeria including Lagos, Adamawa, Delta, River, Cross River, FCT, Kano, Bayelsa, Edo, Imo, Plateau, Nasarawa, Niger, Oyo, Ekiti and Ondo.
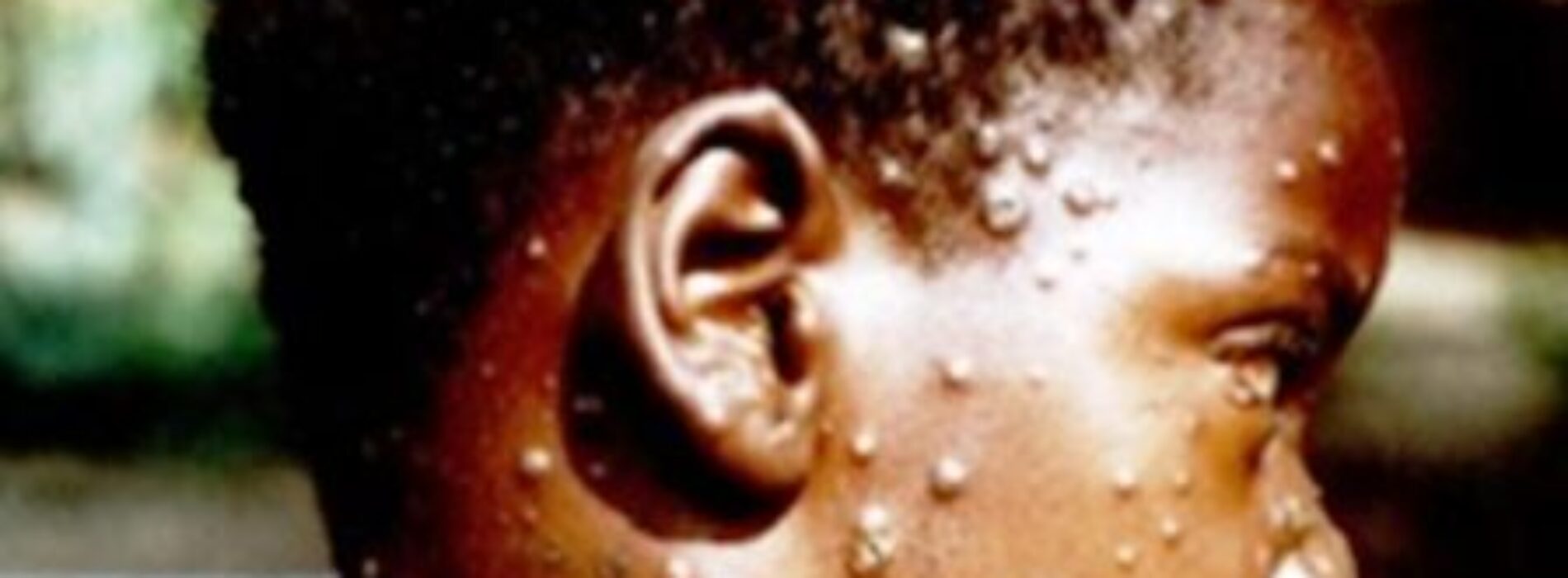
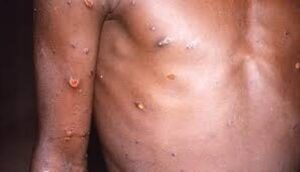
People with monkeypox get a rash that may be located on or near the genitals (penis, testicles, labia, and vagina) or anus (butthole) and could be on other areas like the hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth.
- The rash will go through several stages, including scabs, before healing.
- The rash can initially look like pimples or blisters and may be painful or itchy.
Other symptoms of monkeypox can include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Muscle aches and backache
- Headache
- Respiratory symptoms (e.g. sore throat, nasal congestion, or cough)
You may experience all or only a few symptoms
- Sometimes, people have flu-like symptoms before the rash.
- Some people get a rash first, followed by other symptoms.
- Others only experience a rash.
How long do monkeypox symptoms last?
Monkeypox symptoms usually start within 3 weeks of exposure to the virus. If someone has flu-like symptoms, they will usually develop a rash 1-4 days later.
Monkeypox can be spread from the time symptoms start until the rash has healed, all scabs have fallen off, and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
If You Have a New or Unexplained Rash or Other Symptoms…
- Avoid close contact, including sex or being intimate with anyone, until you have been checked out by a healthcare provider.
- If you don’t have a provider or health insurance, visit a public health clinic near you.
- When you see a healthcare provider, wear a mask, and remind them that this virus is circulating in the area.
Courtesy: US Centre for Disease Control and Prevention
Key facts from WHO
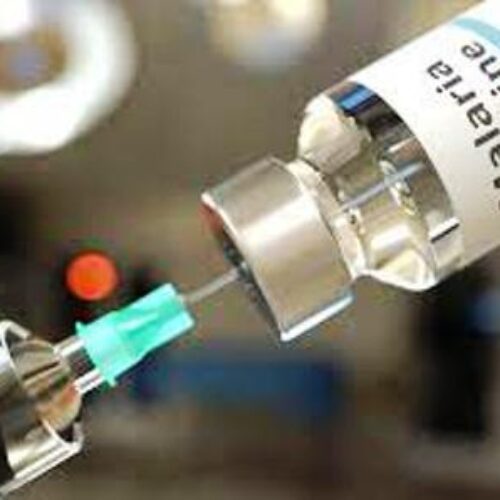
- Vaccines used during the smallpox eradication programme also provided protection against monkeypox. Newer vaccines have been developed of which one has been approved for prevention of monkeypox
- Monkeypox is caused by monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae.
- Monkeypox is usually a self-limited disease with the symptoms lasting from 2 to 4 weeks. Severe cases can occur. In recent times, the case fatality ratio has been around 3–6%.
- Monkeypox is transmitted to humans through close contact with an infected person or animal, or with material contaminated with the virus.
- Monkeypox virus is transmitted from one person to another by close contact with lesions, body fluids, respiratory droplets and contaminated materials such as bedding.
- Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease that occurs primarily in tropical rainforest areas of central and west Africa and is occasionally exported to other regions.
- An antiviral agent developed for the treatment of smallpox has also been licensed for the treatment of monkeypox.
- The clinical presentation of monkeypox resembles that of smallpox, a related orthopoxvirus infection which was declared eradicated worldwide in 1980. Monkeypox is less contagious than smallpox and causes less severe illness.
- Monkeypox typically presents clinically with fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes and may lead to a range of medical complications.







0 Comments
No Comments Yet!
You can be first to comment this post!